Image © Dmitry – Fotolia.com (under license)
How much sleep are you getting? You may think that staying up late makes you more productive – but it does not. It is counterproductive, slowing you down mentally and physically and also making your body more prone to illness.
As far as the body is concerned, sleeping is so much more than a passive activity. Getting some shuteye allows the neurons to recharge and clean themselves from the by-products of normal cellular activities. Sleep also activates important neuronal connections that might otherwise deteriorate from lack of activity. Do you wonder why well-rested people look better in the morning? It’s because during deep sleep, cells have increased production and reduced breakdown of proteins necessary for cell growth and damage repair. Other than having the desired effects of “beauty sleep”, they are also less cranky and more sociable because deep sleep help maintain optimal emotional and social functioning. [1]
Here’s a standard chart of sleep needed:
Newborns (1 to 2 months) – 14 to 18 hours
Infants (3 to 11 months) – 13 to 16 hours
Toddlers (1-3 years) – 12 to 14 hours
Children 3-5 years – 11 to 13 hours
Children 5-12 years – 10 to 11 hours
Teens (13 to 17 years) – 9 to 10 hours
Adults (18 and over) – 7 to 9 hours
Building up on “sleep debt” is literally suicide as you put your body at risk. It doesn’t take more than a week of sleep deprivation for it to alter the activity of over 700 human genes. If prolonged further, the number of affected genes will climb seven times higher. These genes are involved in controlling inflammation, immunity, metabolism, and the response to stress. [2]
Effects of Sleep Deprivation
1. Impairs cognitive abilities: Neuroimaging evidence suggests that sleep deprivation may particularly affect certain parts of the prefrontal cortex region of the brain. Studies show that sleep loss and poor-quality sleep cause deficits in concentration, abstracting ability, problem solving ability, attention, alertness, and vigilance. Creative and innovative performance are also degraded by lack of sleep. [3]
These effects on cognition not only reduce academic or job performance but also cause accidents and injuries. Slow reaction time caused by drowsiness is a big public safety hazard on the road. Skimping on a night’s sleep robs the neurons of the opportunity to recharge for optimal performance, leaving you drowsy and lousy the next day.
It is interesting to note that both too much and too little sleep are found to affect cognition. A Harvard-based study on women reports that undersleepers and oversleepers were estimated to be mentally two years more aged than those who got sufficient hours of sleep. [4]
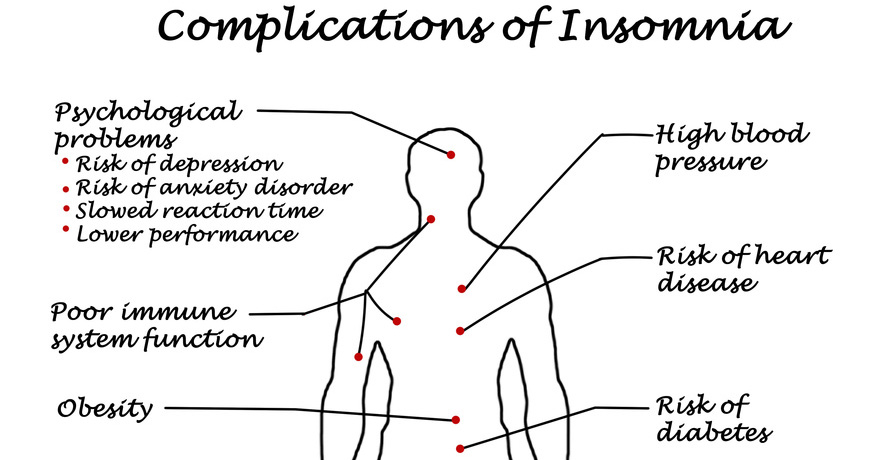
2. Leads to Serious Medical Conditions: Lacking sleep on a regular basis is associated with long-term serious health problems such as diabetes, high-blood pressure, and heart disease. Studies have revealed that sleep deprivation is linked with certain physiological changes including increased blood pressure, impaired control of blood glucose, and increased inflammation.
Adults over the age of 45 who slept fewer than 6 hours per night, was found to be twice as likely to have a stroke or heart attack compared to people who slept 6 to 8 hours per night. [5]
Its adverse impact on insulin sensitivity and appetite regulation may also increase the risk of obesity and diabetes in both children and adults. [6]
The immune system is also at risk as sleep deprivation inhibits immune functions. Sleep and the circadian rhythm were found to have a strong regulatory influence on the immune system. Resulting from the lack of sleep and abnormal sleep patterns, the defense mechanism becomes less responsive due to decrease in the count of white blood cells. [7]
3. Lowers Sex Drive: Research shows that decrease in sex drive due to sleep deprivation affects both genders. Due to low energy, fatigue, and sleepiness, sleep deprived couples would rather catch some Z’s than do the act. [8]
Reduced vigor could also be the result of low testosterone caused by sleep loss, according to a study. [9] The study found that the testosterone levels of men who slept less than five hours a night for one week had significantly lowered than when they had sufficient sleep.
4. Ages Your Skin: There is such thing as beauty sleep. In a study participated in by women, the results show that lack of sleep affects facial appearance especially the features related to the mouth, eyes, and skin. [10]
In another study, it was discovered that sleep quality affects skin function and aging. Sleep deprived individuals showed increased signs of skin aging and slower recovery from the environmental stressors that affect the skin. Poor sleepers also had worse assessment of their general facial appearance. [11]
5. Lowers Your Ability to Manage Stress: A well-rested person is just better at everything, including stress management. The more stressors you have to deal with, the earlier you need to hit the sack.
A study has found a link between sleep deprivation and lower scores on total EQ, intrapersonal functioning, interpersonal functioning, stress management skills, and behavioural coping. The study suggests that sleep loss produces temporary changes not only on the analytical functions of the prefrontal lobe but also on the behavioural and emotional. [12]
6. Causes Decreased Hopefulness and Sociability: Diminished positive mood and increase in negative mood states has been linked with sleep deprivation. This phenomenon can happen to anyone, including children. [13] Sleep deprivation can be caused by apnea and other sleep disorders, and everyone can experience negative effects such as morning headaches, increased irritation, and persistent sleepiness throughout the day. Serious changes to emotion, mood states, and their regulation are influenced by the brain’s serotonergic system or the system responsible for the production of serotonin. Serotonin plays a key role in emotional stability and sleep patterns, which explains why an imbalance in serotonin due to sleep deprivation could also cause mood changes. Accordingly, sleep deprived individuals are more likely to display inappropriate behaviour and act impulsively. [14]
7. Increased Risk of Death: A study revealed that sleeping less than 6 hours a night can make a person 12% more likely to die prematurely than someone with good sleeping habits. But sleep too much and your risk for early death will increase up to 30%. The conducted research suggests that the hours of sleep should be neither too less nor too much. [15]
Sleep deprivation interferes with the biological processes vital for overall health. Consequently, researchers have identified a relationship between sleep deprivation and serious illnesses including some of the top cancers in the U.S., namely breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers. [16]
Other than health risks, sleep deprivation could also make you more prone to injury and even death. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration has reported an estimate of 1,550 deaths and 71,000 injuries caused by sleep-related accidents. [17]
Our bodies are like machines that need constant maintenance and repair. Unfortunately, the benefits of a good night’s sleep are frequently overlooked. A well-rested individual is so much more capable of facing the pressures and living long enough to enjoy his/her success.
5 Tips For Better Sleep Naturally:
How To Make A Herbal “Sleep Like A Rock” Tincture
20 Foods To Help You Sleep Better
Top 10 Essential Oils for Sleep And Insomnia
7 Scientific Reasons Why Sleeping Naked Is Really Good For You
References:
[1] https://ninds.nih.gov/disorders/brain_basics/understanding_sleep.htm
[2] https://www.surrey.ac.uk/features/lack-sleep-alters-human-gene-activity
[3] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21075236
[4] https://health.harvard.edu/blog/little-sleep-much-affect-memory-201405027136
[5] https://sleepfoundation.org/sleep-news/how-sleep-deprivation-affects-your-heart
[6] https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4394987/
[7] https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3256323/
[8] https://webmd.com/sleep-disorders/excessive-sleepiness-10/10-results-sleep-loss
[9] https://uchospitals.edu/news/2011/20110531-sleep.html
[10] https://journalsleep.org/viewabstract.aspx?pid=29095
[12] https://sleep-journal.com/article/S1389-9457(07)00256-0/fulltext?mobileUi=0
[13] https://www.1800cpap.com/a-guide-for-parents-of-children-with-sleep-apnea
[14] Bianchi, Matt T. Sleep Deprivation and Disease: Effects on the Body, Brain and Behavior. New York: Springer, 2014.
[15] https://nhs.uk/news/2010/05May/Pages/lifespan-link-to-sleeping-habits.aspx
★ Get My Books - 100% FREE:
😳 Tinnitus And Brain Health?
After 47 years of studies and countless brain scans done on more than 2,400 tinnitus patients, scientists at the MIT Institute found that in a shocking 96% of cases, tinnitus was actually shrinking their brain cells.
As it turns out, tinnitus and brain health are strongly linked.
Even more interesting: The reason why top army officials are not deaf after decades of hearing machine guns, bombs going off and helicopter noises…
Is because they are using something called "the wire method", a simple protocol inspired by a classified surgery on deaf people from the 1950s...
★ How To Get Rid Of Nail Fungus:
★ Does Your Salad Contain This Vegetable?
★ 20 Natural Painkillers In Your Kitchen (Video):
★ Men's Prostate Health:

2. Famous Chef Sheds 60lbs Researching New Paleo Recipes: Get The Cookbook FREE Here
3. #1 muscle that eliminates joint and back pain, anxiety and looking fat
4. 7 odd foods that KILL your abdominal fat (surprising fat-fighters)
5. The TRUTH about bread (Will surprise you!)
6. [PROOF] Reverse Diabetes with a "Pancreas Jumpstart"
7. Here's What Happens When You "Unlock Your Hip Flexors"
8. The #1 WORST food that CAUSES Faster Aging (beware -- Are you eating this?)
The #1 Muscle That Eliminates Joint And Back Pain, Anxiety And Looking Fat
By Mike Westerdal CPT
Can you guess which muscle in your body is the #1 muscle that eliminates joint and back pain, anxiety and looking fat?
This is especially important if you spend a significant amount of time sitting every day (I do, and this really affects me in a big way!)
Working this "hidden survival muscle" that most people are simply not training because no-one ever taught them how will boost your body shape, energy levels, immune system, sexual function, strength and athletic performance when unlocked.
If this "hidden" most powerful primal muscle is healthy, we are healthy.
Is it...
a) Abs
b) Chest
c) Glutes
d) Hip Flexors
Take the quiz above and see if you got the correct answer!
P.S. Make sure you check out this page to get to know the 10 simple moves that will bring vitality back into your life:
If you enjoyed this page: