Photo – Wikipedia – lic. under CC 3.0
Photo – Wikipedia – lic. under CC 3.0
A study by Stanford discovered that mealworms could offer a solution to our growing plastic problem. [1] Two studies co-authored by Wei-Min Wu, a senior research engineer in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering at Stanford, revealed that mealworms could subsist entirely on Styrofoam and other forms of polystyrene! [2] Apparently, according to Wu’s studies, the mealworm’s gut is filled with microorganisms that are able to biodegrade polyethylene, a common form of plastic. [3] The papers were published in Environmental Science and Technology with co-authors Professor Jun Yang and his doctorate student Yu Yang of Beihang University.
In an interview with CNN, Wu revealed that their findings are revolutionary. [4] It “is one of the biggest breakthroughs in environmental science in the past 10 years,” he said. He believes that their findings could solve the plastic pollution problem that is plaguing our world.
Plastic Use Continues To Increase
In 2008, our global plastic consumption was at 260 million tons. By 2013, an estimated 299 million tons of plastic were produced globally, which is a 4 percent increase over 2012. By the end of 2015, worldwide plastic consumption was at 297.5 million tons. The most shocking part? Every year, 8 million metric tons of plastic end up in our oceans. [5]
Plastics are typically manufactured from crude oil, cellulose, coal, salt, and natural gas. [6] We are so dependent on plastic because it is a versatile, flexible, lightweight, strong, moisture resistant, and relatively cheaper alternative. However useful plastic may seem to us, its major downside is it takes so long to degrade. On average, a plastic bottle takes 450 years to completely degrade, while some bottles even take up to 1,000 years to biodegrade. [7] As a result, our landfills are slowly filling up with plastic and soon, it will become too much to handle. This is where the mealworm comes in.
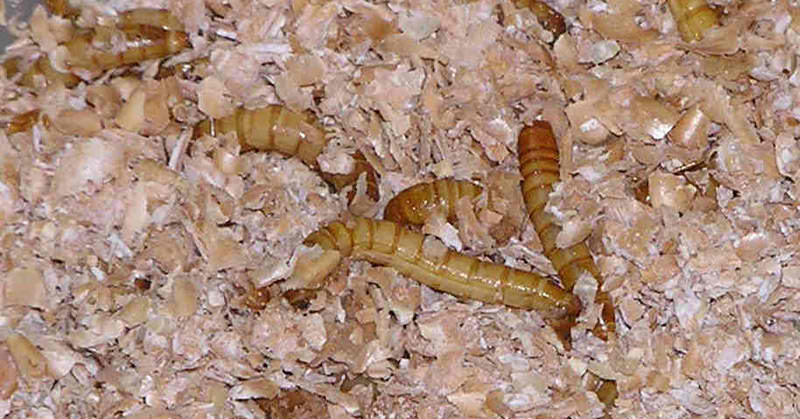
A mealworm is the brown, worm-like larva of the darkling beetle. [8] It is the second stage out of four of the darkling beetle’s life cycle. They exist to eat and grow until the time they have enough energy to begin their transformation into pupae. Mealworms are typically found in warm, dark, and damp places like under decaying leaves and logs. They like to burrow around and will eat grains, vegetation, spoiled food, and other types of fresh and decaying organic matter.
Wu’s research documented 100 mealworms that consumed a total of 34 to 39 milligrams of Styrofoam per day. This is around the same weight as an average pill. Moreover, the mealworms who were exclusively fed Styrofoam were as healthy as those that were eating a regular diet! The worms were able to convert half of the Styrofoam into carbon dioxide. The other half of their waste was worm biomass and biodegradable waste. The tremendous news is that the mealworms’ waste appeared to be safe to use as soil for crops.
The magic lies in the mealworm’s guts. Apparently, the bacteria found within it are essential to degrade plastic. This was demonstrated in an experiment: Mealworms that were fed antibiotics before the plastic were not able to degrade the plastic. Hopefully, by understanding the mechanisms found in the mealworm’s gut, scientists and engineers can figure out new ways of degrading plastic waste.
Another group of researchers, led by Craig Criddle, a senior fellow at the Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment, are also collaborating with Jun yang of Beihang University, as well as other Chinese researchers. [1] They want to study whether the microorganisms found within mealworms and other similar insects can biodegrade plastics such as polypropylene, microbeads, and bioplastics. Polypropylene is used in various products ranging from automotive components to textiles; microbeads are used in most exfoliants; while bioplastics are derived from biomass sources such as biogas methane or corn.
According to the EPA, Americans throw away around 25 billion Styrofoam cups every year. [9] Styrofoam, aka polystyrene, is a synthetic polymer and it can take decades or even centuries to deteriorate. Styrofoam can and does get into animal digestive tracts. According to Douglas McCauley from the University of California, polystyrene foam lodged in animal intestines could be lethal. [10]
McCauley continued to elaborate that even sea turtles or fish could also ingest the very same polystyrene foam. Eventually, these creatures “may be ending up back on our tables.” As harmful as this is to the animals we eat, the same is true for us humans. Styrofoam waste is a bigger problem than most of us realize and when it enters the food chain, we end up eating it. What goes around, comes around.
While these findings are a breakthrough in our pollution problem, more research is still required with the mealworms and plastic. Hopefully, scientists will be able to fully isolate the enzymes found within mealworms to decompose the plastic so that recycling plants and landfills could use them to slowly get rid of our plastic problems. As an alternative, recycling plants and landfills could even just let the mealworms feed directly on the plastic waste.
References:
[1] https://news.stanford.edu/2015/09/29/worms-digest-plastics-092915/
[2] https://profiles.stanford.edu/wei-min-wu
[3] https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.est.5b02661
[4] https://edition.cnn.com/2015/09/30/us/styrofoam-eating-mealworms-plastic-waste/
[5] https://plastic-pollution.org/
[6] https://www.reference.com/science/ingredients-plastic-9e6f89b8455e5b89
[7] https://postconsumers.com/education/how-long-does-it-take-a-plastic-bottle-to-biodegrade/
★ Get My Books - 100% FREE:
😳 Tinnitus And Brain Health?
After 47 years of studies and countless brain scans done on more than 2,400 tinnitus patients, scientists at the MIT Institute found that in a shocking 96% of cases, tinnitus was actually shrinking their brain cells.
As it turns out, tinnitus and brain health are strongly linked.
Even more interesting: The reason why top army officials are not deaf after decades of hearing machine guns, bombs going off and helicopter noises…
Is because they are using something called "the wire method", a simple protocol inspired by a classified surgery on deaf people from the 1950s...
★ How To Get Rid Of Nail Fungus:
★ Does Your Salad Contain This Vegetable?
★ 20 Natural Painkillers In Your Kitchen (Video):
★ Men's Prostate Health:

2. Famous Chef Sheds 60lbs Researching New Paleo Recipes: Get The Cookbook FREE Here
3. #1 muscle that eliminates joint and back pain, anxiety and looking fat
4. 7 odd foods that KILL your abdominal fat (surprising fat-fighters)
5. The TRUTH about bread (Will surprise you!)
6. [PROOF] Reverse Diabetes with a "Pancreas Jumpstart"
7. Here's What Happens When You "Unlock Your Hip Flexors"
8. The #1 WORST food that CAUSES Faster Aging (beware -- Are you eating this?)
The #1 Muscle That Eliminates Joint And Back Pain, Anxiety And Looking Fat
By Mike Westerdal CPT
Can you guess which muscle in your body is the #1 muscle that eliminates joint and back pain, anxiety and looking fat?
This is especially important if you spend a significant amount of time sitting every day (I do, and this really affects me in a big way!)
Working this "hidden survival muscle" that most people are simply not training because no-one ever taught them how will boost your body shape, energy levels, immune system, sexual function, strength and athletic performance when unlocked.
If this "hidden" most powerful primal muscle is healthy, we are healthy.
Is it...
a) Abs
b) Chest
c) Glutes
d) Hip Flexors
Take the quiz above and see if you got the correct answer!
P.S. Make sure you check out this page to get to know the 10 simple moves that will bring vitality back into your life:
If you enjoyed this page: