10 Super Tips For A Great Night’s Sleep. Graphic © herbshealthhappiness.com. Illustration Wikipedia – lic. under CC 3.0
What are you doing up this late? Get to bed this minute! 😉 Seriously though – a good night’s sleep is very important in maintaining your health. Sleep is the time when the body needs to rest – and interestingly, some significant “deep healing” processes take place when we are asleep. Bad sleep quality affects awareness, memory, and coordination – [1] which can ultimately affect a person’s decision making and ability to perform daily tasks at home, work, or school. Sleep deprivation can also be extremely dangerous: Fatigue has been considered a contributing factor in up to 50 percent of motor vehicle accidents in the United States. [2] Also worthy of note – sleep makes you better looking. You will be even more gorgeous when you are all rested. 😉 Here are 10 science-supported tips for improving sleep quality:
1) Have a consistent sleeping schedule.
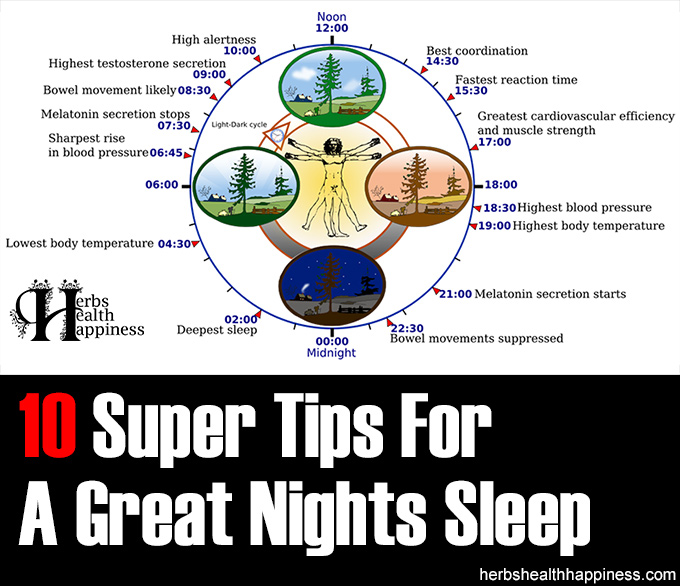
Have a fixed time for continuous, un-interrupted sleep and maintain this schedule for both bedtime and waking time strictly every day. A study was conducted in 2011 by Sharkey, et. al. which revealed that a fixed sleep schedule was able to normalize circadian rhythm. [3] Circadian rhythm is fascinating and can affect our performance in numerous ways – see image below:
 Some features of the human circadian (24-hour) biological clock – Image YassineMrabet (Wikipedia) lic. under CC 3.0
Some features of the human circadian (24-hour) biological clock – Image YassineMrabet (Wikipedia) lic. under CC 3.0
2) Have quality “me-time” to relax before bed.
Relaxing before bed can be done in a variety of ways. Taking a shower or having a bath can help alleviate the stresses from the day and prepare you for rest. Even a short back massage has been proved to reduce anxiety and promote comfort, which is beneficial in initiating and maintaining sleep. [4][5]
3) Avoid doing any “mentally stimulating” activities while settling down.
When you do other activities in bed like reading or doing homework –activities that require you to stay away and concentrate – the increased stimulation can also affect how easy you initiate sleep and maintain it. [6] A 2015 study revealed that using mobile phones negatively affected sleep duration and bedtime. [7]
4) Set up a relaxing atmosphere in your bedroom.
Disturbances from the sleeping environment are one of the major factors that contribute to lack of adequate sleep. Noises from the street, television, or even housemates can be disruptive to the normal sleep cycle. [8] Keep your bedroom quiet and well-insulated from unwanted noise. Another tip borrowed from Feng Shui (this one seems to work really well!) is to remove all objects from the bedroom that are associated with other activities than bedroom activities. The bedroom should contain only objects that are directly related to rest, relaxation and love. It should also if possible contain only colors that you find restful and enjoyable. Another fun experiment to try is to align the bed with the head facing north as some believe this is associated with better dreams…
5) Avoid eating before going to bed.
Eating a full meal 1 to 2 hours before bed can hinder your sleep instead of promote it. A study in 2007 revealed that a full meal four hours before bedtime was able to shorten sleep onset compared to the same meal given an hour before (instead of four). [9]
6) Avoid drinking or eating anything with caffeine at least four to six hours before your bedtime.
Because of coffee’s caffeine content, it’s consumed by people all over the world to keep themselves awake. Caffeine keeps a person alert and awake, [10] which explains why it’s detrimental to a good night’s sleep.
7) Avoid drinking alcohol before bed.
According to a study in 2005 on sleep hygiene, alcohol intake before bed (as well as smoking), was a factor associated with poor sleep quality and insomnia. [11]
8) Avoid taking long naps during the day.
A review of sleep management techniques in 2013 revealed that short 30-minute naps in the after lunch were beneficial in improving sleep quality. [12] Sleep hygiene guidelines by Samuels state that naps should be limited to half an hour and never done after 4 PM. [8]
9) Do regular exercise.
The 2013 review [12] also associates moderate exercise and stretching early morning contributed to better sleep quality and over physical and mental health.
10) Ensure you get much needed sunlight.
Aside from synthesizing vitamin D, sunlight also helps regulate the sleep cycle. A 2014 study revealed that people who were exposed to less sunlight had poorer sleep quality and overall health. [13]
11) Bonus tip: Clean that bedding.
Delicious fresh sheets and pillowcases are bound to help you feel more comfortable in the night. Another great tip is to wash the pillow. Here’s a super tutorial: How To Wash And Whiten Yellowed Pillows
References:
[1] Ramadan, M. & Al-Saleh, K. (2014). The Association of Sleep Deprivation on the Occurrence of Errors by Nurses Who Work the Night Shift. https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4340449/
[2] Mitler, M., et. al. (2008). The Sleep of Long-haul Truck Drivers. https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2430925/
[3] Sharkey, K., et. al. (2011). Effects of an advanced sleep schedule and morning short wavelength light exposure on circadian phase in young adults with late sleep schedules. https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1389945711001651
[4] Chen, W., et. al. (2013). Effect of Back Massage Intervention on Anxiety, Comfort, and Physiologic Responses in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure. https://online.liebertpub.com/doi/abs/10.1089/acm.2011.0873
[5] Shinde, M. & Anjum, S. (2014). Effectiveness of Slow Back Massage on Quality of Sleep among ICU Patients. https://ijsr.net/archive/v3i3/MDIwMTMxMTI0.pdf
[6] Felt, B. & Chervin, R. (2014). Medications for sleep disturbances in children. https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3943656/
[7] Jiang, X., et. al. (2015). Sleep Duration, Schedule and Quality among Urban Chinese Children and Adolescents: Associations with Routine After-School Activities. https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4303432/
[8] Samuels, C. & Alexander, B. (2013). Sleep, Recovery, and Human Performance. https://waterpolo.ca/admin/docs/clientuploads/ltad/Sleep_Recovery_ENG.pdf
[9] Afaghi, A., O’Connor, H. & Chow, C. (2007). High-glycemic index carbohydrate meals shorten sleep onset. https://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/85/2/426.full
[10] National Institute of Health (2014). Caffeine. https://nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/caffeine.html
[11] Jefferson, C., et. al. (2005). Sleep Hygiene Practices in a Population-Based Sample of Insomniacs. https://researchgate.net/profile/Timothy_Roehrs/publication/7593033_Sleep_hygiene_practices_in_a_population-based_sample_of_insomniacs/links/0deec517c4632ba786000000.pdf
[12] Tanaka, H. & Furutani, M. (2013). Sleep Management Promotes Health Lifestyle, Mental Health, QOL, and a Healthy Brain. https://www.google.com.ph/books?hl=en&lr=&id=ubaeBQAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA211
[13] Boubekri, M., et. al. (2014). Impact of Windows and Daylight Exposure on Overall Health and Sleep Quality of Office Workers: A Case-Control Pilot Study. https://aasmnet.org/jcsm/ViewAbstract.aspx?pid=29503
★ Get My Books - 100% FREE:
😳 Tinnitus And Brain Health?
After 47 years of studies and countless brain scans done on more than 2,400 tinnitus patients, scientists at the MIT Institute found that in a shocking 96% of cases, tinnitus was actually shrinking their brain cells.
As it turns out, tinnitus and brain health are strongly linked.
Even more interesting: The reason why top army officials are not deaf after decades of hearing machine guns, bombs going off and helicopter noises…
Is because they are using something called "the wire method", a simple protocol inspired by a classified surgery on deaf people from the 1950s...
★ How To Get Rid Of Nail Fungus:
★ Does Your Salad Contain This Vegetable?
★ 20 Natural Painkillers In Your Kitchen (Video):
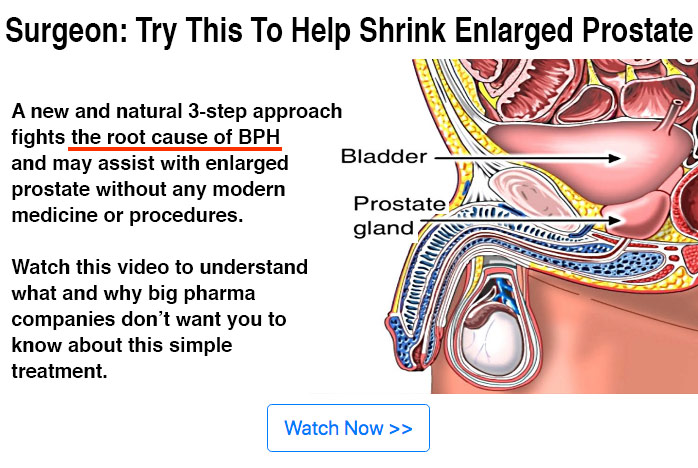
★ Men's Prostate Health:

2. Famous Chef Sheds 60lbs Researching New Paleo Recipes: Get The Cookbook FREE Here
3. #1 muscle that eliminates joint and back pain, anxiety and looking fat
4. 7 odd foods that KILL your abdominal fat (surprising fat-fighters)
5. The TRUTH about bread (Will surprise you!)
6. [PROOF] Reverse Diabetes with a "Pancreas Jumpstart"
7. Here's What Happens When You "Unlock Your Hip Flexors"
8. The #1 WORST food that CAUSES Faster Aging (beware -- Are you eating this?)
The #1 Muscle That Eliminates Joint And Back Pain, Anxiety And Looking Fat
By Mike Westerdal CPT
Can you guess which muscle in your body is the #1 muscle that eliminates joint and back pain, anxiety and looking fat?
This is especially important if you spend a significant amount of time sitting every day (I do, and this really affects me in a big way!)
Working this "hidden survival muscle" that most people are simply not training because no-one ever taught them how will boost your body shape, energy levels, immune system, sexual function, strength and athletic performance when unlocked.
If this "hidden" most powerful primal muscle is healthy, we are healthy.
Is it...
a) Abs
b) Chest
c) Glutes
d) Hip Flexors
Take the quiz above and see if you got the correct answer!
P.S. Make sure you check out this page to get to know the 10 simple moves that will bring vitality back into your life:
If you enjoyed this page: