10 Warning Signs of Ovarian Cancer Women Shouldn’t Ignore. Graphic © herbshealthhappiness.com. Illustration © AdobeStock 72074117 (under license)
Despite the falling mortality rates for ovarian cancer, it still remains as the fifth most common cancer to affect women and accounts for the highest mortality in cancers that affect the female reproductive system.
Ovarian cancer is regarded as a “silent killer” because symptoms can be subtle and only 20% of cases are discovered early enough for treatment. The American Cancer Society has very scary predictions when it comes to ovarian cancer in 2016 – roughly 21,000 women in the US will become diagnosed while 14,000 women will die from it – that’s two out of every three cases diagnosed.
By 2012, almost 200,000 women in the US were living with ovarian cancer and a familial or personal history of gynecological cancer is a risk factor. The overall risk of becoming affected by ovarian cancer is 1 in 75 while the risk of dying from it is 1 in 100. [1][2]
It pays to be vigilant. Take note of the following warning signs that you may have ovarian cancer.
#1: Irregular Menses
Most women are under the impression that their period should come every month – and more or less it should. However, a woman’s menstrual cycle can occur every 21 to 35 days, which is considered as the “normal” length of a typical menstrual cycle. Be aware if your menstruation doesn’t occur regularly according to your own cycle length. Give or take a few days isn’t bad but when the lapses become weeks to months, you may have a problem with your ovaries. As a women ages, menstrual cycles become more regular and shorter. [3]
![]()
Everyone knows green smoothies are healthy, right? However…
Have you heard of a “red” smoothie? If not, check out this story…

=> “Red” Smoothie Helps Alabama Girl Shed 80lbs!
![]()
#2: Prolonged And Heavy Bleeding
Your menstruation (a.k.a. actual bleeding) should last anywhere between 3 to 7 days. The flow usually starts off weak, then gets heavier, before tapering off. The color adjusts too – from bright to dark red as your bleeding stops. However, prolonged, heavy bleeding from the uterus can signify a problem. The walls of the uterus, called the endometrium, are thickened during the regular ovulatory process and slough off during menstruation if you aren’t pregnant (meaning there is no fertilized egg to embed in the uterine walls). If the walls become too thick, you may experience abnormal, heavy bleeding which can indicate a problem. [3][4]
#3: Bleeding In Between Periods
Persistent bleeding not attributed to the normal ovulatory process is definitely a cause for concern. You will be able to differentiate this from menstrual bleeding because of the color and timing. Bleeding in between periods is usually bright red and doesn’t taper off. You will note that you will still get regular menstruation (between 21 and 35 days) and experience bleeding in between. Like pelvic pain, this kind of bleeding can be due to tissue damage attributed to ovarian cancer.
A popular theory that attempts to explain why ovarian cancer occurs is the “incessant ovulation” theory. When menstrual cycles are very short or if bleeding occurs repeatedly every few days or weeks, the ovary and uterus are consistently “disturbed”. This disruption of the surface cells of the ovary and uterus can damage and mutate its genetic make-up (the underlying cause of any cancer) and can hasten the growth of tumors. [5] Note any other vaginal abnormalities and be sure to report these also to your healthcare professional.
#4: Persistent Abdominal Pain
Menstruation can be a very difficult time for some, especially those affected with menstrual cramps aka. dysmenorrhea. Menstrual cramps typically occur right before and during bleeding – for some women, this pain can be severe while others may not feel anything at all. For people with severe menstrual cramps, it can be difficult to tell if the pain is “normal” or not. But remember this – pain that is out of the norm persists even after menstrual bleeding has stopped and even after taking pain medication and performing relaxation techniques, is dangerous. It can signify tissue damage, internal bleeding (inside the abdomen or pelvis), and even tumor growth. Many cases of invasive types of ovarian cancer are associated with abdominal pain that persists longer than 2 weeks. [6][7] Be wary also of persistent, achy, dull pain in the lower back. Many women patients are reminded by this of labor pain.
#5: Urinary Frequency And Urgency
Increased frequency in urination and increased urgency can also be attributed to the growth of an ovarian tumor. Cancer is characterized by the abnormal growth and proliferation of cells, usually presenting as a mass of cancer cells called a tumor. The continued growth of an ovarian tumor can start pressing against the bladder, contributing to an increased urge to void or urinate, as well as frequent urination. [7]
#6: Irregular Bowel Movement
In later stages of cancer, metastases to nearby organs are very common. When ovarian cancer cells have invaded the small and large intestines, it can manifest as irregular and difficult bowel movement. Be wary of alternating constipation and diarrhea. Invasive types of ovarian cancer can even present as bleeding in the stool. [7]
#7: Abdominal Bloating
Abdominal pain and irregular bowel movement are often accompanied by abdominal bloating and stiffness, or the persistent feeling of “being full” or “gassy”. This can be due to (1) increased gas or (2) ascites. When ovarian cancer has invaded the surrounding tissues in the abdominal cavity, it changes the permeability of the intestinal walls, causing an influx of gas and fluid in the abdominal space. Increasing abdominal girth is considered one of the most common symptoms of ovarian cancer. [8]
#8: Loss Of Appetite
Ovarian cancer is reported to cause a sudden loss of appetite that is markedly out of character for the person affected. Pressure from the tumor itself can cause poor appetite and notably for the person to feel full very quickly. [8]
Because the symptoms of ovarian cancer often occur simultaneously with each other, difficulty eating and abdominal bloating are two that go hand in hand.
#9: Increased Urinary Frequency And Urgency
Urinary issues, for example, sudden urges to urinate and urination that is more frequent than usual can be an indication of many things, ovarian cancer included. In the case of ovarian cancer, this can include bouts of complete loss of bladder control that get progressively worse over several weeks.
#10: Sudden, Unexplained Weight Loss
Compared to other forms of cancer, cachexia (cancer-related weight loss) manifests in ovarian cancer more prominently. Poor appetite and abdominal bloating coupled with the nutrition and energy stolen by cancer cells make weight loss rapid and more noticeable. The rapid growth and spread of cancer cells take a lot out of the body, affecting the body’s normal balance of energy and nutrition – leading to severe weight loss.
Survival Due To Early Detection
The earlier ovarian cancer is detected, the higher a woman’s chance of survival. If you take note of these warning signs and immediately seek medical help if you experience one or several of them, your chances of becoming an ovarian cancer survivor are actually very high. The following are the chances of survival upon detection of each stage of ovarian cancer: stage I (93%), stage II (70%), stage III (37%), and stage IV (25%). [9]
Goff’s study in 2007 revealed that the symptoms of pelvic pain, urinary frequency, and urgency, abdominal bloating, and difficulty in feeding were positively correlated with ovarian cancer if anyone occurred greater than 12 times a month consistently, in less than a year. [8]
The Truth About CA-125
If you are at risk for ovarian cancer (especially if you have a familial history of it), your doctor may ask for a sample of your blood to test for CA-125. CA-125 stands for cancer antigen 125, a protein, specifically a tumor marker, that is present in the blood when a person is affected by ovarian cancer. Higher values suggest a progressive form of cancer while lower values suggest the opposite – because of this, CA-125 is used for monitoring effectiveness of on-going cancer treatment.
However, CA-125 cannot diagnose cancer alone. The presence of this tumor marker can be found in women with uterine fibroids and other similar conditions as well. This is why other examinations need to be done to fully diagnose and stage ovarian cancer; a biopsy of the affected tissue and histopathology are still the golden standards in diagnosing any form of cancer. [10][11]
Note: As with the rest of this website, this article is not medical advice nor a substitute for a consultation with a medical professional. We do not advise self-diagnosis or self-treatment. If you believe you have the symptoms mentioned or are concerned about your health, please schedule an appointment with your doctor/healthcare advisor.
References:
[1] American Cancer Society. What are the key statistics about ovarian cancer? https://cancer.org/cancer/ovariancancer/detailedguide/ovarian-cancer-key-statistics
[2] National Cancer Institute. SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Ovary cancer. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/ovary.html
[3] Mayo Clinic. Menstrual cycle: What’s normal, what’s not. https://mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/menstrual-cycle/art-20047186
[4] Hapangama, D. & Bulmer, J. (2016). Pathophysiology of heavy menstrual bleeding. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26695831
[5] Cramer, D. (2012). The Epidemiology of Endometrial and Ovarian Cancer. https://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3259524/
[6] US National Library of Medicine. Painful menstrual periods. https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003150.htm
[7] Bankhead, C., Kehoe, S. & Austoker, J. (2005). Symptoms associated with diagnosis of ovarian cancer: a systematic review. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2005.00572.x/full
[8] Goff, B., et. al. (2007). Development of an ovarian cancer symptom index. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cncr.22371/full
[9] Holschneider, C. & Berek, J. (2000). Ovarian cancer: Epidemiology, biology, and prognostic factors. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/1098-2388(200007/08)19:1%3C3::AID-SSU2%3E3.0.CO;2-S/abstract
[10] Mayo Clinic. CA 125 test. https://mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/ca-125-test/basics/definition/prc-20009524
[11] US National Library of Medicine. CA-125 blood test. https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/007217.htm
★ Get My Books - 100% FREE:
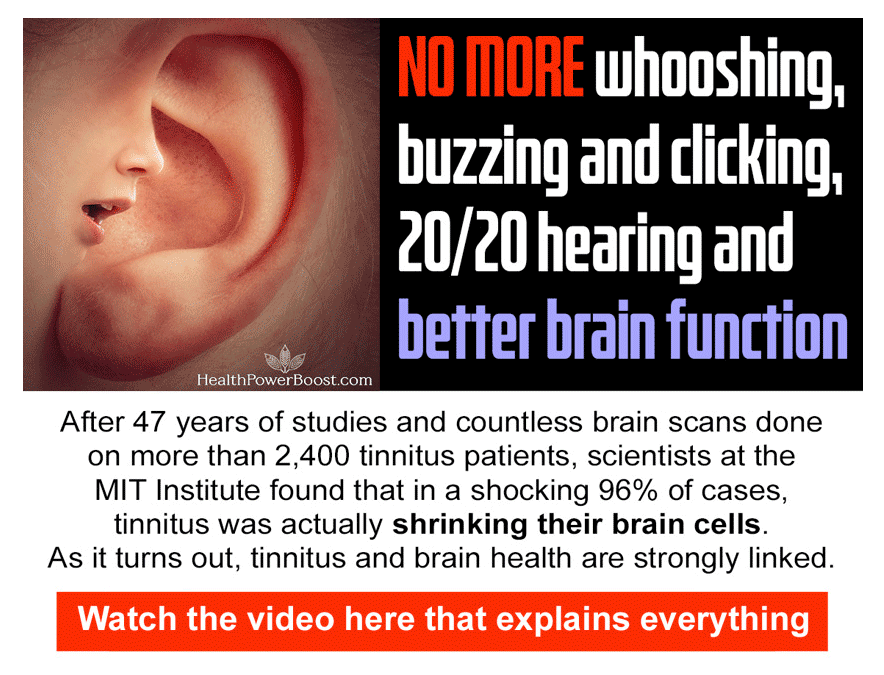
😳 Tinnitus And Brain Health?
After 47 years of studies and countless brain scans done on more than 2,400 tinnitus patients, scientists at the MIT Institute found that in a shocking 96% of cases, tinnitus was actually shrinking their brain cells.
As it turns out, tinnitus and brain health are strongly linked.
Even more interesting: The reason why top army officials are not deaf after decades of hearing machine guns, bombs going off and helicopter noises…
Is because they are using something called "the wire method", a simple protocol inspired by a classified surgery on deaf people from the 1950s...
★ How To Get Rid Of Nail Fungus:
★ Does Your Salad Contain This Vegetable?
★ 20 Natural Painkillers In Your Kitchen (Video):
★ Men's Prostate Health:

2. Famous Chef Sheds 60lbs Researching New Paleo Recipes: Get The Cookbook FREE Here
3. #1 muscle that eliminates joint and back pain, anxiety and looking fat
4. 7 odd foods that KILL your abdominal fat (surprising fat-fighters)
5. The TRUTH about bread (Will surprise you!)
6. [PROOF] Reverse Diabetes with a "Pancreas Jumpstart"
7. Here's What Happens When You "Unlock Your Hip Flexors"
8. The #1 WORST food that CAUSES Faster Aging (beware -- Are you eating this?)
The #1 Muscle That Eliminates Joint And Back Pain, Anxiety And Looking Fat
By Mike Westerdal CPT
Can you guess which muscle in your body is the #1 muscle that eliminates joint and back pain, anxiety and looking fat?
This is especially important if you spend a significant amount of time sitting every day (I do, and this really affects me in a big way!)
Working this "hidden survival muscle" that most people are simply not training because no-one ever taught them how will boost your body shape, energy levels, immune system, sexual function, strength and athletic performance when unlocked.
If this "hidden" most powerful primal muscle is healthy, we are healthy.
Is it...
a) Abs
b) Chest
c) Glutes
d) Hip Flexors
Take the quiz above and see if you got the correct answer!
P.S. Make sure you check out this page to get to know the 10 simple moves that will bring vitality back into your life:
If you enjoyed this page: